Research & insights
Browse the articles below for thought leadership, data-driven insights and reports published by Huq using its own primary data.
Browse the articles below for thought leadership, data-driven insights and reports published by Huq using its own primary data.
Submit the form below to access your free location intelligence report for - instantly!
Your Report for is available for download.
Click to DownloadSubmit the form below to access your free location intelligence report for - instantly!
Your Report for is available for download.
Click to DownloadBook a live demo!
Book a consultation with one of our location experts.
Interested in insights about a specific area or the UK as a whole? Share your request, and we’ll provide a data file for your location.
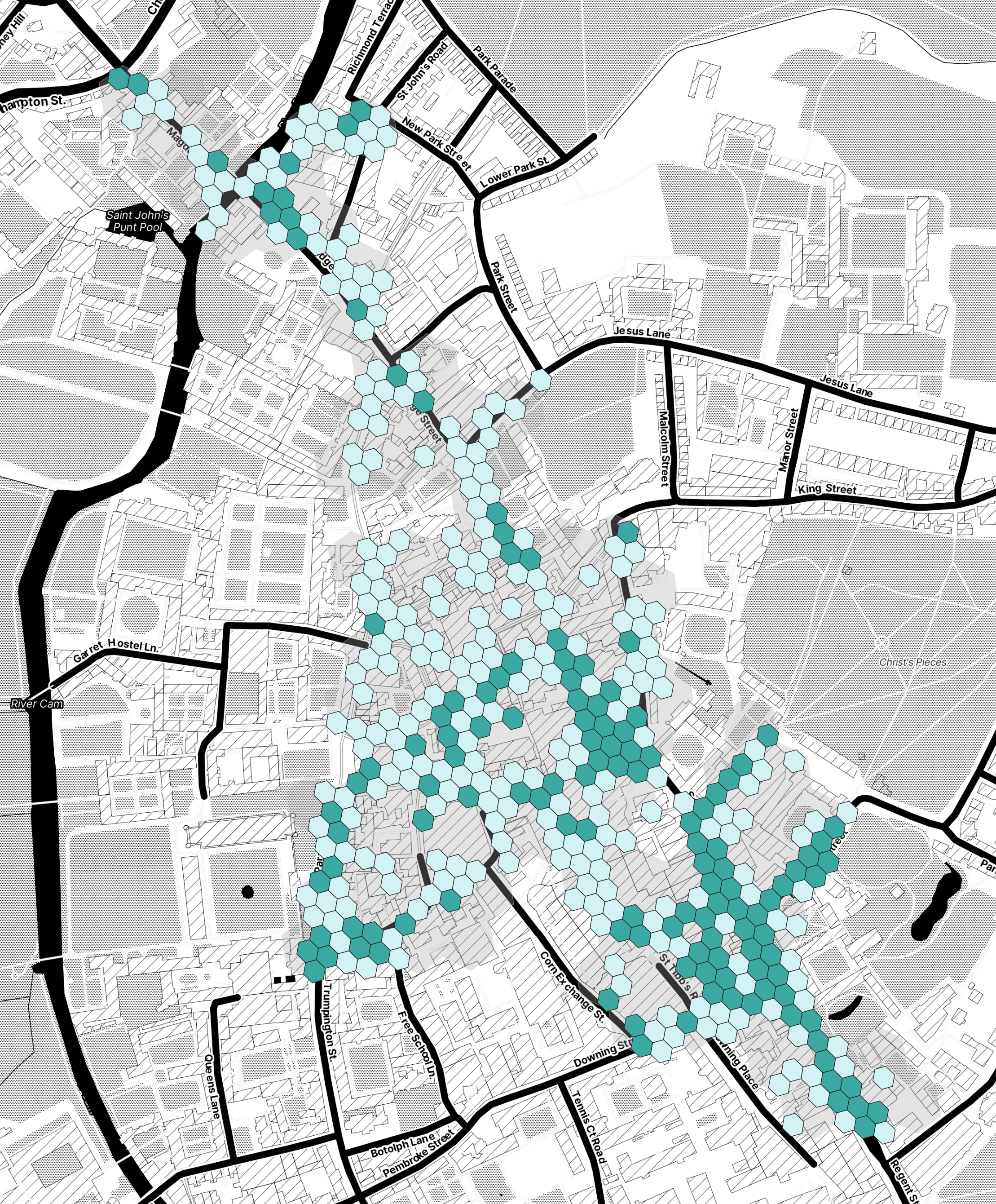

Great! Your request has been received. Now you can download the case study using the link below.
Want to keep reading? Close and return to module page